agentic_rag_101
🔹🔹 🔹🔹 🔹🔹 
Agentic Retrieval Augmented Generation or Agentic RAG is quickly becoming a popular approach in AI, as it combines the strengths of retrieval systems with the smart decision-making of agents. This makes it possible for large language models (LLMs) to pull in real-time data and use it to improve their answers. By doing this, these systems become more flexible and can handle more complex, ever-changing tasks.
Section 1: Understanding RAG and Agents
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a method used to improve LLMs by giving them access to real-time data. Normally, LLMs rely only on the data they were trained on, which can become outdated. RAG fixes this by allowing models to retrieve information from external sources, like databases or live web searches. This way, when the model is asked a question, it can pull in fresh, relevant data and combine it with its own knowledge to create a more accurate and useful response. RAG is especially valuable in areas like customer support or finance, where up-to-date information is crucial.
Agents, on the other hand, are systems that can make decisions and act on their own. In AI, agents are used to manage tasks and processes, automatically adjusting to whatever situation they are in. They can assess what needs to be done, choose the best way to do it, and then carry out the task, making them very flexible and efficient.
Enter Agentic RAG!
Section 2: What is Agentic RAG?
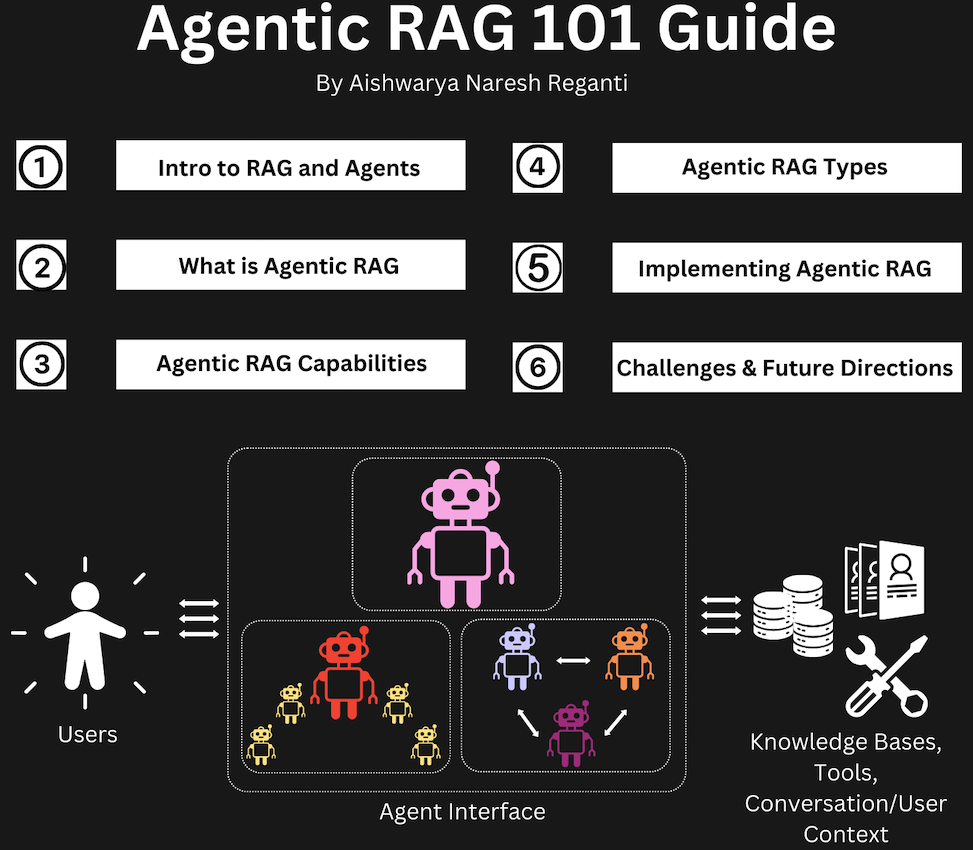
When RAG and agents are combined, the agents take charge of the entire process, deciding how and when to retrieve the data and how to use it to generate the best possible response. Instead of simply retrieving information, the agents make smart choices about where to get the data, what is most important, and how to integrate it into the LLM’s answer. This results in a system that can handle more complex queries and deliver responses that are both accurate and tailored to the specific situation.
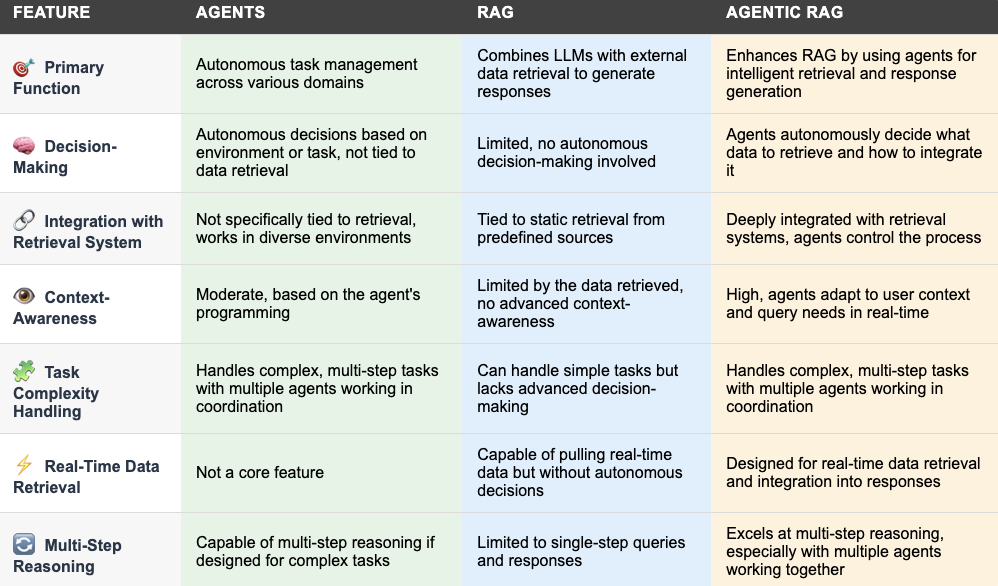
The table below provides a clear overview of how Agents, RAG, and Agentic RAG differ in terms of their key features and functionalities:
🔹🔹 🔹🔹 🔹🔹 
How Agentic RAG Works – Step-by-Step Example
Let’s walk through an example to understand how Agentic RAG operates in real-time. Suppose you’re using a customer support chatbot powered by Agentic RAG to resolve an issue with your internet service. The query you input is:
"Why is my internet slow in the evenings?"
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
- User Query
- You type your query into the chatbot: "Why is my internet slow in the evenings?"
- The query is received by the system, which activates the intelligent agent to determine the next steps.
- Agent Analyzes the Query
- The agent analyzes your question, recognizing that it’s a service-related query that might need data on your internet usage patterns, network traffic, and potential service disruptions.
- Based on this, the agent identifies relevant data sources, such as your service history, network reports, and real-time traffic data.
- Agent Decides on Retrieval Strategy
- The agent determines which external data sources to query. In this case, it may decide to:
- Fetch data from your account history to check if there are any noted service issues.
- Retrieve network traffic reports from the internet service provider (ISP) to analyze peak usage times in your area.
- Query a public knowledge base to gather information on common causes of evening slowdowns.
- The agent determines which external data sources to query. In this case, it may decide to:
- Data Retrieval
- The retrieval system, directed by the agent, pulls information from multiple sources. It fetches:
- Your service history, showing an uptick in complaints during the evening.
- Network traffic reports indicating high congestion in your neighborhood between 6 PM and 10 PM.
- Articles from the knowledge base explaining how peak-time usage and congestion can cause slower speeds.
- The retrieval system, directed by the agent, pulls information from multiple sources. It fetches:
- LLM Generates Response
- Once the relevant data is retrieved, the large language model (LLM) processes it. The model takes into account both its pre-trained knowledge and the real-time data fetched by the agent.
- The LLM generates a response that integrates these insights:"It appears that your internet speed slows down in the evenings due to high traffic in your area during peak hours. You might want to consider upgrading your plan or using the internet during off-peak times to avoid congestion."
- Response Delivery
- The generated response is delivered to you, providing a clear and accurate explanation of why your internet is slow in the evenings, based on both real-time data and the model’s general understanding of network congestion.
- Follow-Up Actions
- If necessary, the agent could continue assisting by offering additional solutions. For instance, it could recommend a faster internet plan or schedule a technician visit if it detects any ongoing issues with your connection.
Key Points of Agentic RAG in Action:
- The agent autonomously decides which sources to query based on your question.
- The retrieval system pulls real-time data specific to your query, enhancing the LLM’s response.
- The LLM generates an answer that is more accurate and context-aware because it integrates both pre-trained knowledge and the fresh data fetched by the agent.
Note that while this is a basic example of how Agentic RAG operates, it can also interact with not just knowledge bases but also other tools and services, similar to the way traditional agents do.
Section 3: Agentic RAG Capabilities
Agentic RAG offers a range of powerful features that make it an attractive option for systems requiring dynamic, real-time data retrieval and decision-making. Here are some of the standout features:
-
Dynamic Data Retrieval
One of the main features of Agentic RAG is its ability to fetch real-time information based on user queries. By incorporating intelligent agents, the system can decide which data sources to query, ensuring the most relevant and up-to-date information is retrieved. This allows for more accurate and contextually aware responses, especially in environments where data changes frequently, like news or finance.
-
Autonomous Decision-Making
In a traditional RAG setup, the retrieval process is relatively straightforward. However, in Agentic RAG, intelligent agents make autonomous decisions throughout the pipeline. They determine what data to retrieve, when to retrieve it, and how to use it, all without the need for human intervention. This autonomy makes the system more flexible and adaptable, allowing it to handle a wide range of complex tasks efficiently.
-
Context-Aware Responses
Agentic RAG doesn’t just retrieve information blindly. Agents assess the context of each query and adjust the retrieval process accordingly. This means that the system can tailor responses based on the specific needs of the user, improving relevance and accuracy. The agents consider the context in real-time, allowing the system to respond more intelligently to nuanced queries.
-
Scalability
With agents taking control of the retrieval and decision-making processes, Agentic RAG scales more effectively than traditional RAG systems. It can handle more complex queries across different domains by leveraging multiple data sources and balancing workloads intelligently. The system is designed to expand in complexity and volume while maintaining performance, making it suitable for large-scale applications like customer support or enterprise search.
-
Reduced Hallucination Risk
One of the challenges with traditional LLMs is hallucination, where the model generates incorrect or nonsensical responses. Since Agentic RAG pulls real-time data and intelligently integrates it into responses, the likelihood of hallucinations is significantly reduced. The agents ensure that the information used is accurate and relevant, lowering the chance of the system providing false information.
-
Customizable Workflows
Agentic RAG allows for highly customizable workflows based on the task or domain. Agents can be fine-tuned to follow different retrieval strategies, prioritize certain data sources, or adapt to specific business needs. This flexibility makes the system highly versatile, capable of functioning effectively in different industries or application settings.
-
Multi-Step Reasoning
Agentic RAG pipelines can handle complex tasks that require multiple steps to reach a solution. They can break down a user’s query into smaller steps, retrieve data, and progressively build an answer, allowing for more nuanced and logical responses.
Section 4: Types of Agentic RAG
Agentic RAG systems can be classified based on how agents operate and the complexity of their interactions with the retrieval and generation components. There are several types, each suited for different tasks and levels of complexity:
- Single-Agent RAG
- In this setup, a single intelligent agent is responsible for managing the entire retrieval and generation process. The agent decides which sources to query, what data to retrieve, and how the data should be used in generating the final response.
- This type is ideal for simpler tasks or systems where decision-making doesn’t require much complexity. Single-agent RAG is efficient when managing routine queries with straightforward information retrieval needs.
- Multi-Agent RAG
- Multi-agent RAG involves multiple agents working together, each handling different aspects of the retrieval and generation process. One agent might handle retrieval from a specific source, while another might focus on optimizing the integration of data into the LLM's response.
- Multi-agent systems are well-suited for more complex scenarios, where different types of data need to be fetched from various sources or when tasks need to be broken down into smaller, specialized parts.
- Hierarchical Agentic RAG
- In this setup, agents are organized in a hierarchy, where higher-level agents supervise and guide lower-level agents. Higher-level agents may decide which data sources are worth querying, while lower-level agents focus on executing those queries and returning the results.
- This type is beneficial for highly complex tasks, where strategic decision-making is required at multiple levels. For example, hierarchical Agentic RAG is useful in systems that need to prioritize certain data sources or balance competing priorities.
Section 5: Implementing Agentic RAG
Here are some resources you can use to get started with implementing Agentic RAG.
- https://medium.com/the-ai-forum/implementing-agentic-rag-using-langchain-b22af7f6a3b5
- https://github.com/benitomartin/agentic-rag-langchain-pinecone
- https://www.llamaindex.ai/blog/agentic-rag-with-llamaindex-2721b8a49ff6
- https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/examples/agent/agentic_rag_using_vertex_ai/
- https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2024/07/building-agentic-rag-systems-with-langgraph/
Section 6: Agentic RAG Challenges and Future Directions
As Agentic Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) continues to evolve, it faces several challenges that need to be addressed to reach its full potential. At the same time, there are exciting future directions that promise to make the technology even more powerful and adaptable
Challenges:
- Coordination Complexity
- As systems integrate more agents, ensuring smooth coordination between them becomes more complex. Each agent may operate with different priorities, leading to potential bottlenecks or conflicts in decision-making.
- Inefficient coordination can lead to slower response times or incomplete answers if agents don’t properly sync their retrieval tasks.
- Scalability Concerns
- While agents can make systems more flexible, managing a large number of agents and data sources can be resource-intensive. As the system scales, maintaining real-time performance without sacrificing accuracy becomes more difficult.
- High-latency responses and overburdened retrieval pipelines can diminish the benefits of real-time, dynamic data integration.
- Data Quality and Reliability
- The quality of the retrieved information is crucial for accurate responses. If agents pull data from unreliable or low-quality sources, it could lead to misinformation or inaccurate answers.
- Poor data quality can undermine trust in the system and lead to incorrect decisions, particularly in critical fields like healthcare or finance.
- Agent Decision-Making Transparency
- Understanding and monitoring how agents make decisions about retrieval and data usage can be difficult. Without transparency, it’s challenging to ensure that agents are consistently making optimal choices.
- Lack of transparency can lead to a “black box” effect, where users and developers struggle to interpret why certain decisions were made, making debugging and optimization harder.
Future Directions:
- Improved Agent Collaboration and Orchestration
- Future Agentic RAG systems will focus on better orchestration methods that allow agents to collaborate more efficiently. This includes smarter workflows, where agents can better divide tasks, communicate seamlessly, and resolve conflicts without human intervention.
- This will enable smoother operations, reducing bottlenecks, and ensuring faster, more accurate responses across complex queries.
- Hybrid Human-Agent Systems
- In the future, systems could integrate human oversight, where agents operate autonomously but humans intervene in cases of uncertainty or high stakes. This would allow agents to handle routine queries, while humans handle exceptions or complex situations.
- This would combine the efficiency of agents with human intuition and expertise, especially in areas where the consequences of errors are high, such as legal or medical decisions.
- Learning Agents
- RAG Agents may become more adaptive by incorporating learning mechanisms. Instead of following static rules, agents will be able to learn from past interactions, improving their ability to make decisions over time.
- Learning agents would allow systems to evolve, becoming better at handling new and complex queries as they accumulate more experience, leading to smarter, more personalized interactions.
- Ethical Decision-Making Agents
- As Agentic RAG systems become more integrated into sensitive applications, developing agents that can make ethical decisions will be crucial. These agents will need to consider factors such as fairness, bias mitigation, and responsible AI usage.
- Ethical decision-making agents will help reduce biases in responses, ensure fairness in automated processes, and build trust in AI systems, particularly in sectors like law enforcement or social services.